If you're deciding to grow a vegetable garden, knowing how to prepare soil correctly is crucial. But did you know that the best time to prepare soil is at the end of the growing season? Depending on where you live, this will usually be in early or late fall. Preparing soil during this time will enrich the soil for the next season, in spring. Today we will share some tips and tricks with you where you can firstly identify the type of soil you have an the things you can do to prepare it for the next growing season. Before we get into that, let's take a look and see why preparing soil is crucial.
What is the Importance of Good Soil?

If you're new to gardening, you may think that you can just plant directly in the ground, in your backyard. But, that may not be the case. Gardening soil is not just dirt and pebbles – it's usually amended with minerals and nutrients which your plants feed from. Just like we need nutrients to grow and survive, so do plants. Providing them with a nutrient rich soil is very important, especially if you're growing edible plants, such as herbs, vegetables, or fruits. So how can you make good, quality soil for your plants? First, you'll need to test your soil's pH.
Do a Soil Test
Before you go ahead and amend your soil, it's very important to test the soil yourself, to see exactly what type of soil you already have. Knowing that, you can then go ahead and add the nutrients that the soil may be missing. There are a couple of ways you can do this:
- Purchase an inexpensive soil test kit from your local nursery, hardware store, or online.
- Test the soil yourself with an at home soil pH test that's cheap and quick. This method uses baking soda and vinegar.
Why Does a Soil Test Matter?
Knowing what type of soil you have is crucial to know what you can and cannot grow in your garden. Additionally, it'll help you understand what type of minerals and nutrients your soil may need.
- Knowing the soil's pH will help you determine what you can grow in it. Blueberries, for example, prefer more acidic soil, while alkaline pH soil is best suited for brassicas such as cabbage.
- By knowing whether your soil is neutral, acidic, or alkaline, will help you determine what type of amendments to add to the soil.
- If you have soil that's very acidic or very alkaline, this could be bad for your plants' growth because that means they're not getting enough of certain nutrients.
What is the Best Soil pH?
A pH scale will range from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, 0 being very acidic, and 14 being very alkaline. As a rule of thumb, most store bought garden soils fall between 5 and 9 on the pH scale. Most plants prefer a pH range of 6.0 and 6.5, which is slightly acidic. This is when microbial activity is at its best and the plant's roots can easily access nutrients. That being said, different plants prefer different soil pH ranges, so it's always best to check before.
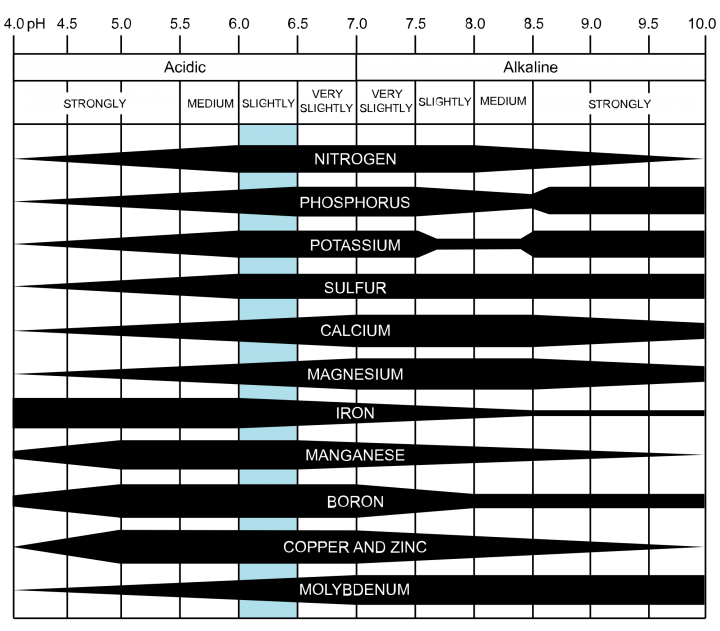
Nutrients at Varying pH Values
This chart shows which nutrients are available at different pH values. As you can see, slightly acidic soil (6.0 to 6.5) is best suited for plants.
How to Adjust the Soil pH
Once you've tested the soil pH, you may find that you need to adjust it, so that it falls between the correct range. Depending on what you're planting, you may need to adjust the soil to make it more acidic or more alkaline:
- Raise soil pH by adding pulverized limestone or wood ash.
- Lower soil pH by adding sulfur, compost, or peat.
The Importance of NPK – Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium
The main nutrients that plants use are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. You will often find these “NPK values” on the packages of fertilizers that you purchase from your local nursery or hardware stores. These NPK values will be shown on a package as follows: N-P-K, where each nutrient will be determined by a number. For example, a fertilizer package may show 20-10-20, meaning there is 20% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 20% potassium.
- Nitrogen (N) helps to produce lush, green leaves, which makes it a much needed nutrient for leafy greens such as lettuce, broccoli, and herbs.
- Phosphorus (P) stimulates root development as well as early plant growth. Phosphorus is particularly important for peppers, squash, cucumbers, tomatoes, and basically any edible plant that that will develop after a flower has been pollinated. You can increase phosphorus in soil by adding bonemeal or slow release rock phosphate.
- Potassium (K) protects plants against diseases, enhances flavor, and promotes overall plant health. Radishes, turnips, carrots, garlic, and onions prefer potassium. Increase potassium in soil by adding wood ashes, gypsum, kelp, or greensand.
Types of Soil
Now that you know the importance of nutrients in the soil, and the soil's pH, it's time to look at the type of soil you may have. This is the structure of the soil, and it's very important at determining how much water the soil holds or how little. Soil that holds too much water is not well draining and can therefore encourage root rot and disease. In terms of gardening soil, there are four different types: sand, silt, clay, or loam. Let's take a closer look at each one of these types of soil.
- Sandy Soil – This type of soil as you may have guessed, contains sand and larger particles. It drains very quickly, but does not hold nutrients as well as other types of soil. Root vegetables grow best in sandy soil as it drains quickly. If you have sandy soil and want to grow other types of vegetables, amend it with aged manure, sawdust, or peat moss.
- Silt Soil – This type of soil has smaller particles than sandy soil, and holds on to nutrients and water for longer. Potted plants and most vegetables can thrive in this soil, so long as proper drainage is provided. To amend silt soil, add pea gravel and compost, coarse sand, or horse manure.
- Clay Soil – This type of soil is very fine and doesn't drain very quickly. In hot summers, this type of soil can harden and become water logged. Properly prepared clay soils are great for cabbage, beans, and other leafy greens. Amend clay soil by adding compost, coarse sand, and peat moss to encourage drainage and add texture to the soil.
- Loamy Soil – This is the best type of soil for growing both fruits and vegetables. This is because loamy soil has a perfect balance of sand, silt, and clay, and easily drains, holds nutrients and moisture, and contains lots of organic matter.
Soil Amendments
Amending your soil can improve it, either by injecting extra nutrients into it or correct the soil pH. Adding organic matter to the soil will generally improve it by moving the pH towards the ideal range for both fruits, vegetables, and herbs. When you see organic matter, it can mean a number of different things, such as decomposed leaves, manure, or regular garden compost. The following soil amendments are used often to adjust the consistency of garden soil:
- Compost: Adds nutrients to the soil and lowers pH.
- Manure: Great soil conditioner and best if composted.
- Bark: Helps to improve soil structure.
- Peat Moss: Helps soil to retain water and lowers pH.
- Leaf Mold: Decomposed leaves help to add nutrients and structure to soil.
- Sand: Helps to improve drainage in clay soil.
- Lime: Raises the pH in acidic soil and also helps to loosen clay soil.
- Top Soil: This will replace the existing soil and is usually used with another soil amendment.
How to Amend Soil With Organic Matter
As we mentioned earlier, it's best to prepare garden soil in the fall, after the season is over. This way, you are preparing your soil for the next season. Do this by first removing any plants, roots, or weeds, that may be in or around the existing soil. Clear the area of any rocks or pebbles. Spread organic matter onto the existing soil, making sure that the depth is at least 2 inches. Leave the organic matter on the surface over the entire winter.
By spring time, you'll find that worms will have made their way into the organic matter. They deposit castings (waste), which helps to add nutrients and enrich the soil. A few weeks before planting, work the organic matter in with the soil using a rake, and you're ready to plant! Now that you know how to prepare soil for garden, it's time to roll up your sleeves and get to gardening!


















